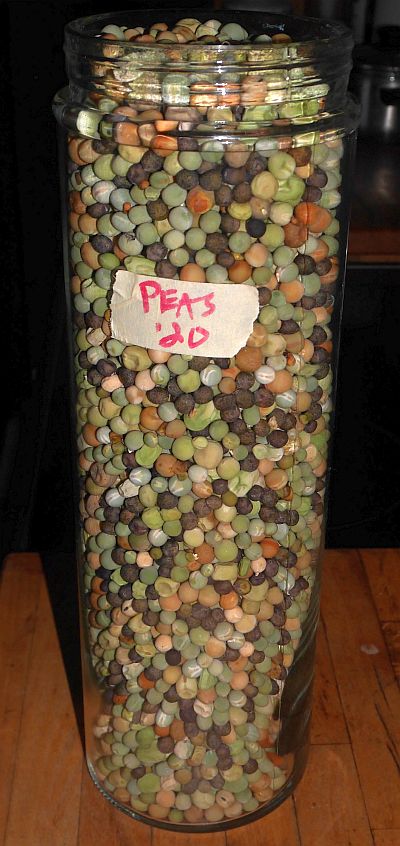
Of the 20 varieties of peas we grew this year in my garden and the community garden, some of the harvest is saved for seed and sharing in Norwegian Seed Savers (https://kvann.no). The rest are mixed for winter soups and pea fritters. Here’s some of this year’s crop:

Category Archives: Heirlooms
2020 Potato Harvest
Here’s 24 of the 26 potato varieties I grew this year. Many are from the national potato preservation project administered by the Norwegian Seed Savers (KVANN). 10 different varieties(mini-tubers) which have been cleaned for virus are offered every year. Some of the smaller ones are small as they were started from mini-tubers (used as seed potatoes next year).
The varieties are from left to right:
TOP ROW: Tysk Blå; Eggeplomme; Gjernes potet; Sverre; Rosenpotet; Lange’s potet; Ingeleivs; King Edward Troll
SECOND ROW: Ivar; Blå Kerrs Pink; Gamle Raude; Svart Valdres; Buddhisten fra Snåsa; Ringerikspotet; Svartpotet fra Vegårshei (syn. Blå Kongo); Abundance
BOTTOM ROW: Beate; Rocket; Shetland Black; Sharpe’s Express; Brage; Hroar’s Drege and Sarpo Tominia
 I’m not head-banging to the potatoes….honest:
I’m not head-banging to the potatoes….honest: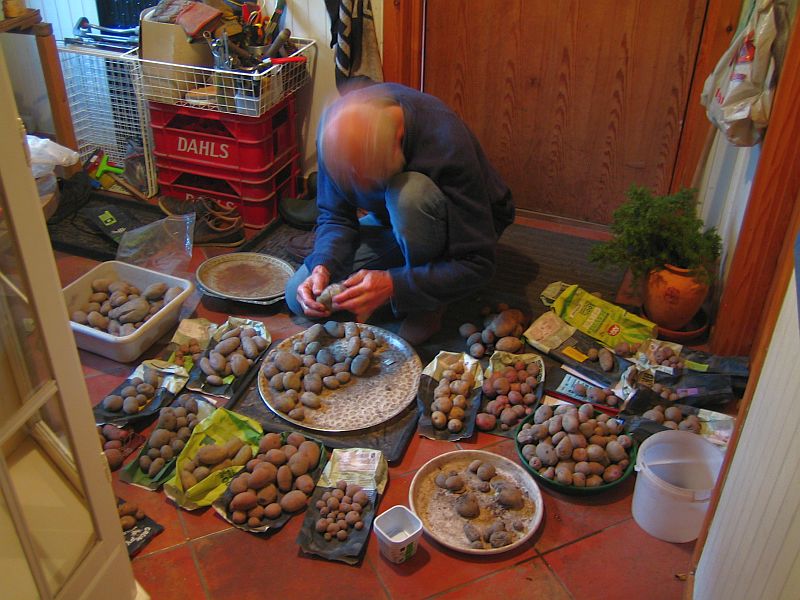


Artikler om grønnsaksarven fra Hagetidend
English: In 2011, I wrote a series of one page articles about Norwegian heirloom vegetables in Norsk Hagetidend (the magazine of the Norwegian Horticultural Society) in Norwegian. The complete series can be found below.
- Fjellmandel og takløk (Mandel potato and the roof onions of Gudbrandsdal)
2. Aleksandra hvitløk (Garlic Aleksandra)
3. Hagemelde “Backlund-Bly” fra USA (Garden orach Backlund-Bly from Seed Savers Exchange i USA)
4. Stjernemelde (Caucasian spinach, Hablitzia tamnoides)
5. Vossakvann (Voss Angelica)
6. Seiersløk fra Lofoten (Victory onion, Allium victorialis from Lofoten)
7. Luftløk fra Udøy (Walking onion, Allium x proliferum from the island Udøy and Catawissa onion)
8. Jordskokk fra Ontario (Jerusalem artichoke from Ontario that travelled the world)
9. Maries høje ært (Marie’s pea…from Norway to Denmark and back)
10. Tante Cis tomat (Tante Cis or Ansofs Gule tomat)
On the World’s Vanishing Vegetables
I had become a member of HDRA following a “chance” encounter on a train north to Edinburgh where I was studying. I was travelling with a bike as was a guy called Dave du Feu. Dave was and still is heavily involved in cycle campaigning. On that journey he told me of the Edinburgh Cycle Campaign, Spokes and introduced me to organic gardening and the HDRA, both of which I joined!




Kvann foredrag i Trondheim
Etter foredraget begynte møtelederen faktisk å fortelle forsamlingen om at det var til og med dannet en forening KVANN…før jeg kunne fortelle dette selv… Jeg kunne derfor sto opp og fortelle at jeg var faktisk KVANNs leder og jeg fortalte litt om oss….
Her er hele foredrag til Ingerid:
KVANN-2017.11.11a
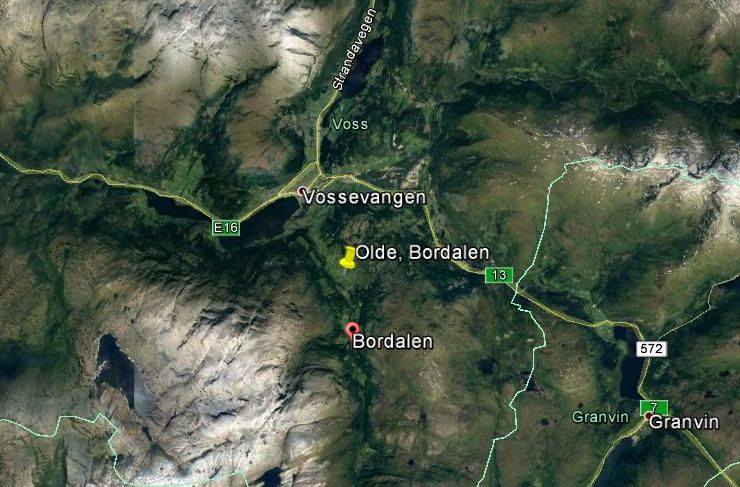
Kvannsafari to Olde in Bordalen
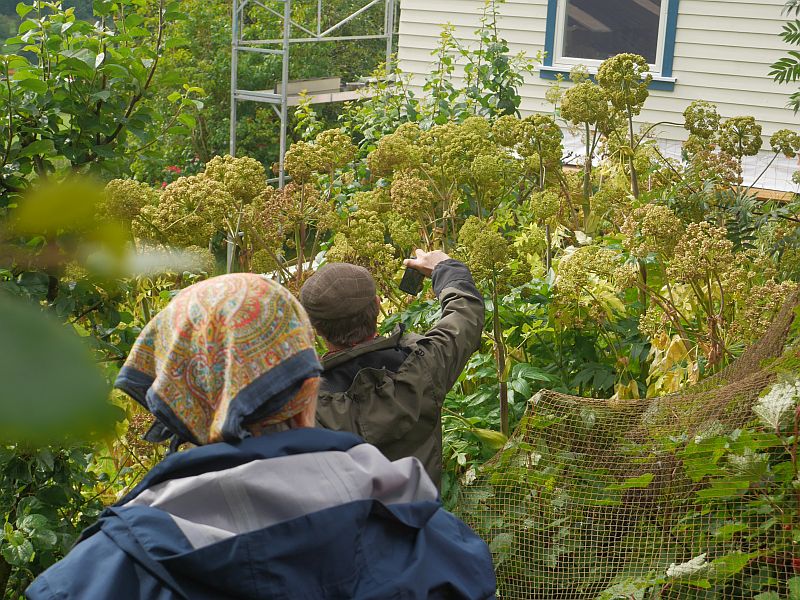
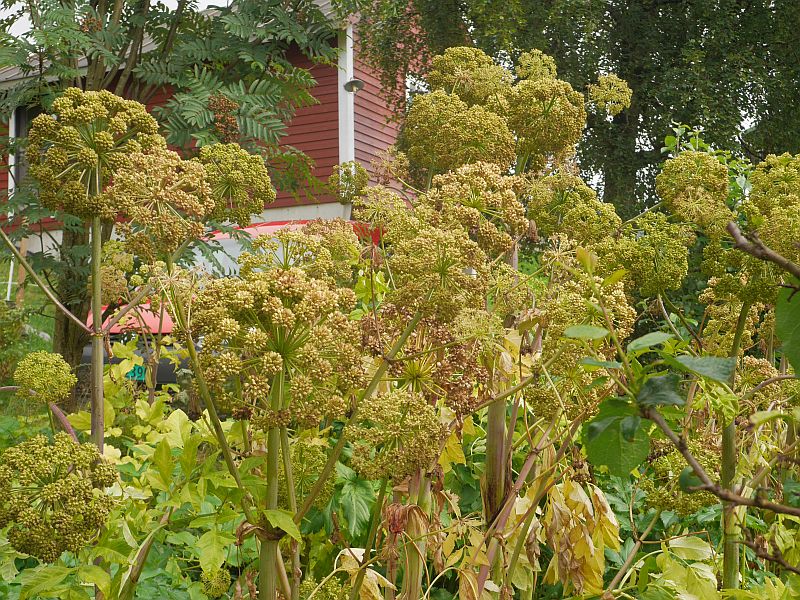
Kvann is Norwegian Mountain Angelica, Angelica archangelica ssp. archangelica, one of the most important plants in Norwegian history, used as a vegetable back to the times of the Vikings and an important exported medicinal herb in the past. It was a very important vegetable of the Sami people! In my book “Around the World in 80 plants”, I tell the story of a special form of kvann, known as Vossakvann, traditionally cultivated in special Kvann-yards (kvannagard) on the farms in this area. A good historical review of this plant can be found in Ove Fosså’s paper (see below) and, in Norwegian, please search for Vossakvann on Norwegian Seed Savers web site, http://kvann.no).
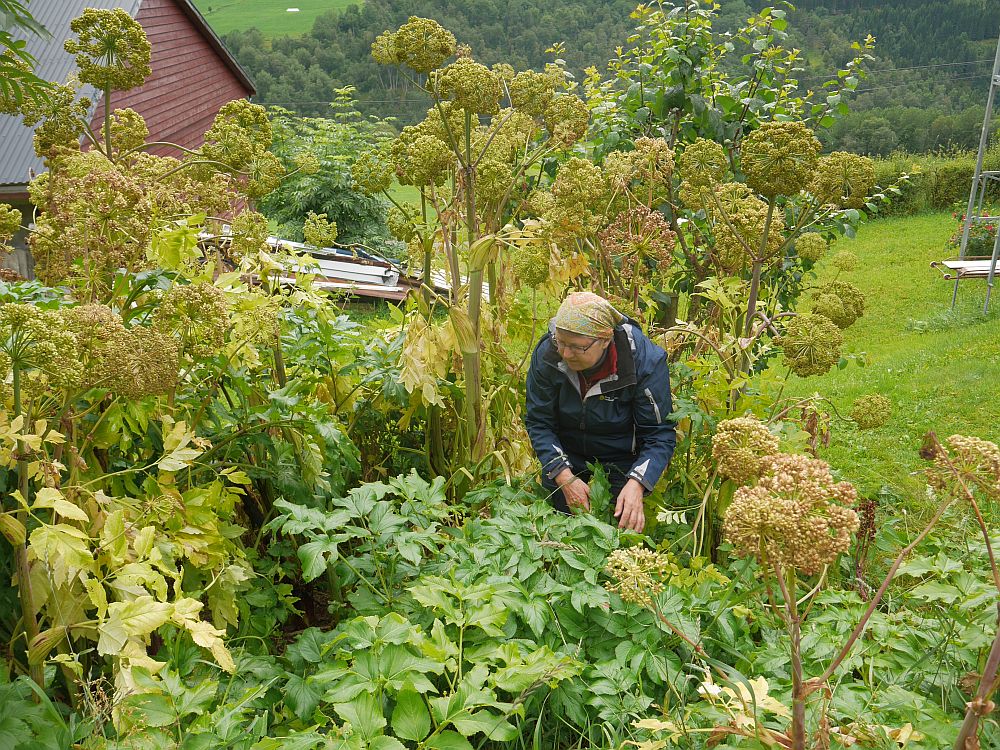
The aim of our trip was to visit one of the last farms still growing Vossakvann, Olde in Bordalen. Vossakvann has almost filled (solid) leaf and flower stalks whilst wild plants are hollow …in other words, there’s more “flesh”… It is also milder tasting, perhaps because there’s more flesh, the plant producing the same amount of bitter substances which are spread over a larger volume?
Jorunn Ringheim Hernes, who had recently retired from Landbruksrådgivning (the agricultural advisory service) in Voss, had arranged with the farmer, Knut Arvid Olde, to visit. Some years ago, Jorunn had sent me a couple of plants from a different line of Vossakvann, Elgje. Sadly, this line had recently been lost due to the seed not germinating. Further, a third line at Markusteigen has almost disappeared locally due to the fact that the kvannagard had not been looked after (repeatedly cut down) and only 3-4 plants could be found on a visit there last week. The farmer is now aware of this and will try to look after and build up the kvannagard again! The Markusteigen line is the one line from which plants still exist away from Voss (in Oslo and in Orkanger) (seed were collected a few years ago).
I’d heard that Knut Arvid Olde was enthusiastic to conserve this unique variety on the farm and this was confirmed during our visit, although there was a sense of panic in his voice when he heard that his kvannagard was the only one left, partly as he had planned to sell some of the harvest to a local cheese producer! There were about 30 flowering stalks full of seeds and below the plants many self-sowed young plants. I was surprised that all the young plants I tested had solid stalks and Knut Arvid said that they hadn’t selected for this property… I had previously learned that only a percentage of seed propagated plants had the characteristics of Vossakvann, but here they all seemed to be true to form!
Jorunn Hernes will return in a week or two to collect seed during drier weather (it was wet during our visit and only a few seed were ripe). Landbruksrådgivning also have a project to make a trial kvannagard and Knut Arvid was positive that it could be on his land using his line!
Norwegian Seed Savers is, confusingly here, called KVANN (see http://kvann.no) as this is our most important native useful plant traditionally. We have a project, coordinated by Stephen Barstow and Åsmund Asdal and new web pages are planned) in which we are trying to conserve the different lines of Vossakvann with help of the seed saver network and perhaps also further develop a more stable cultivar.