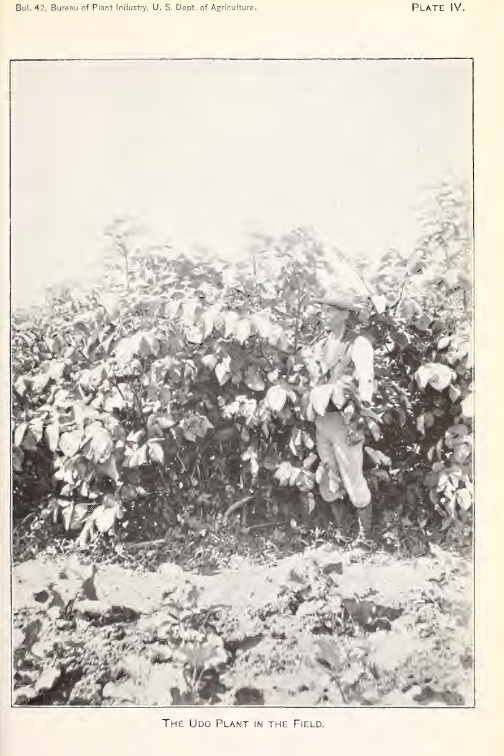
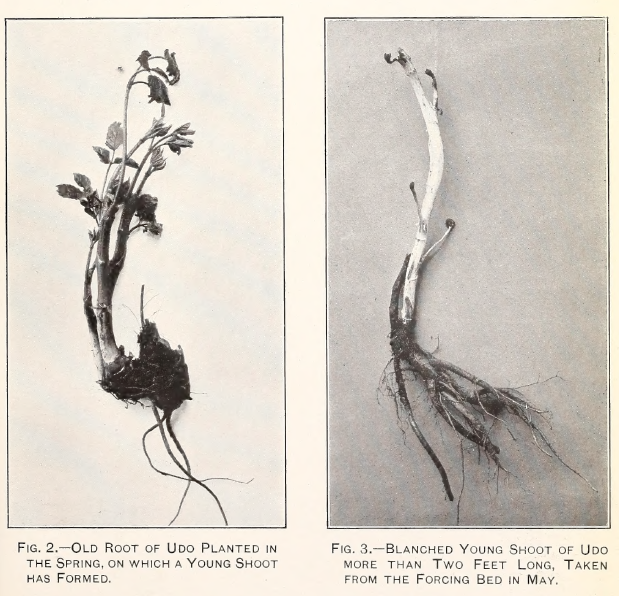
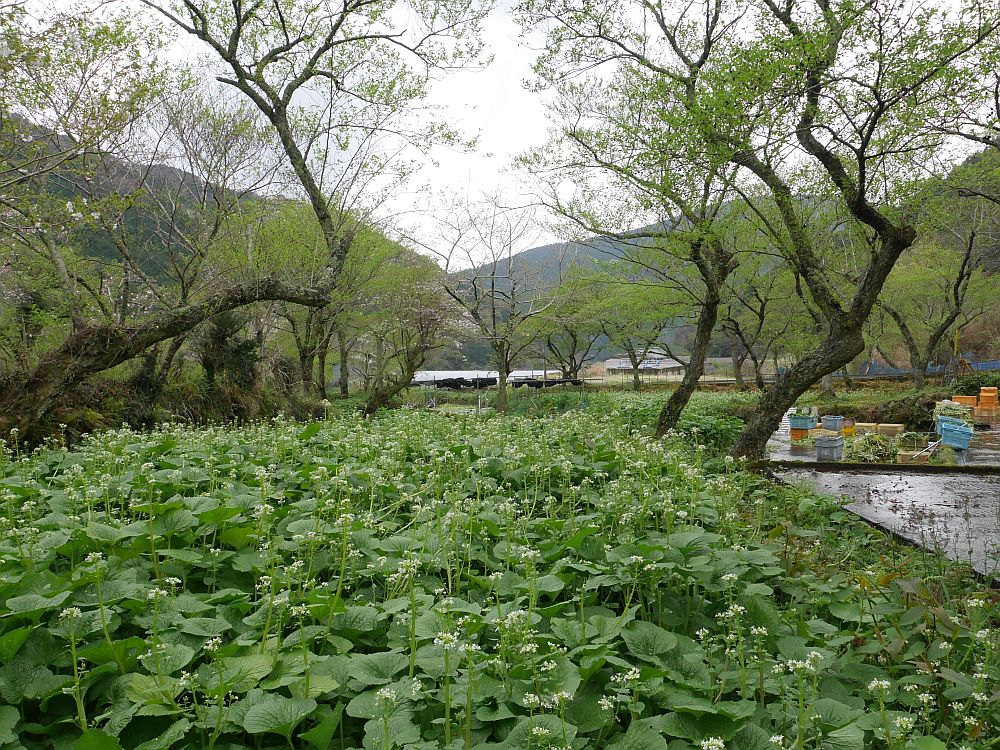
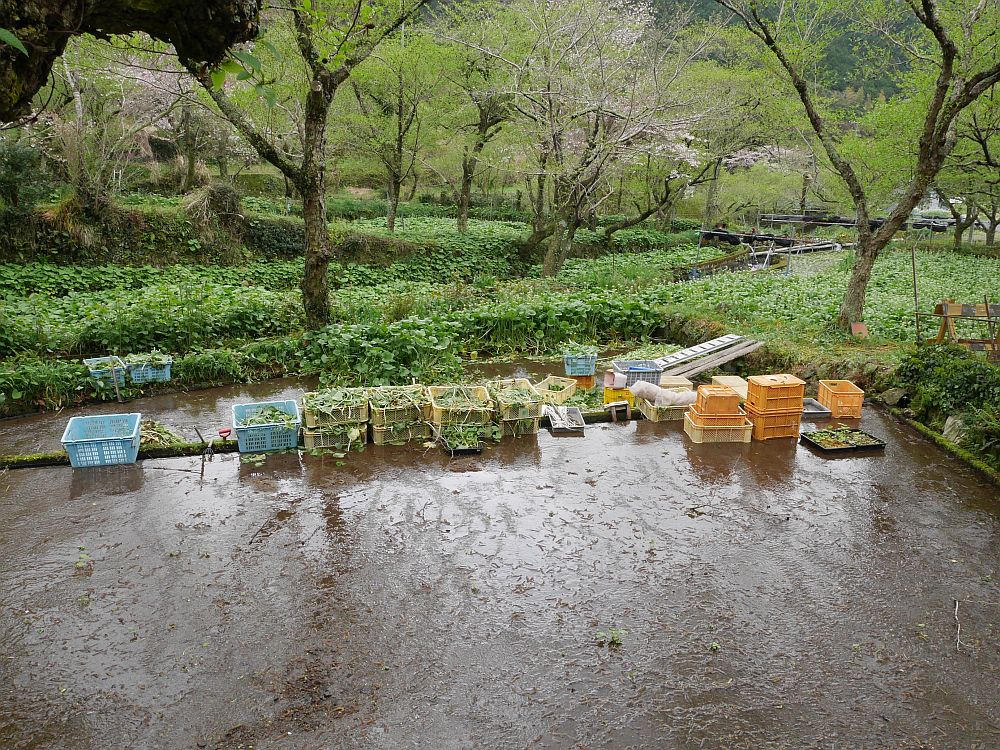
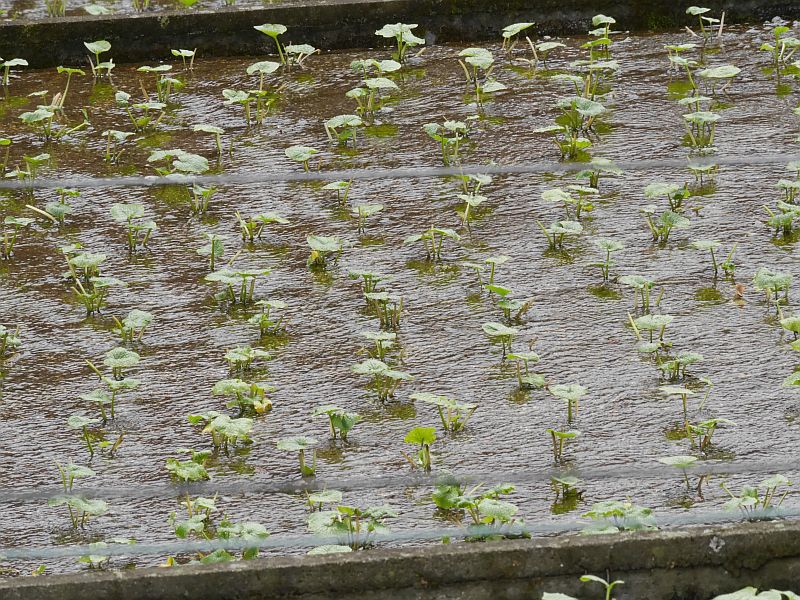
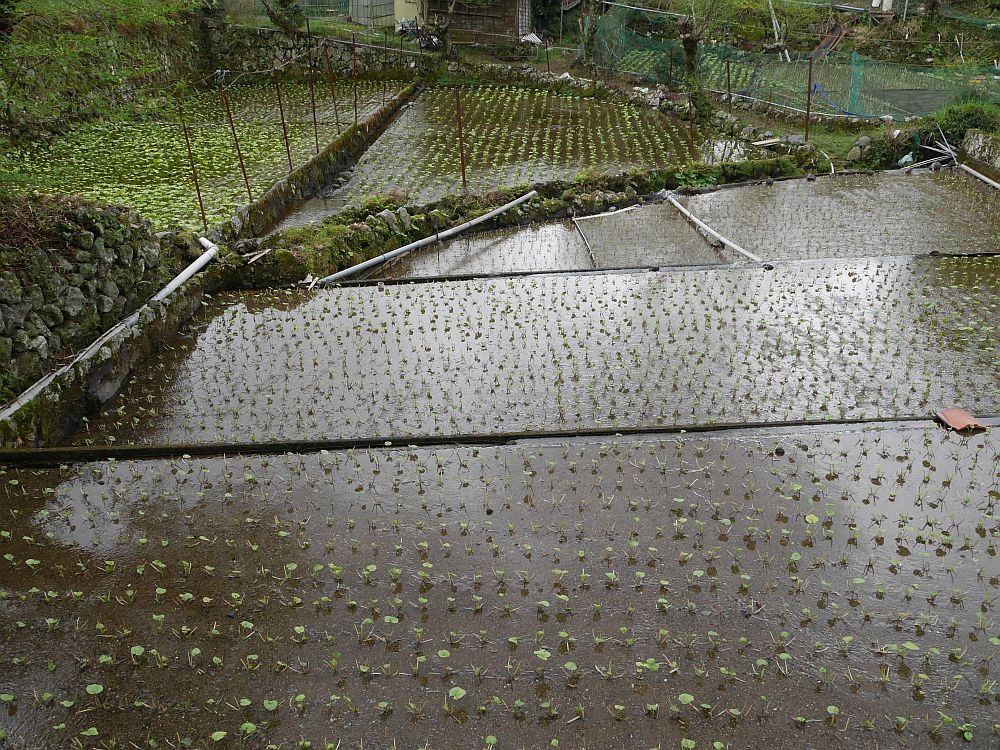
I stumbled upon this interesting US Department of Agriculture Bulletin from 1903 by David Fairchild, who calls himself Agricultural Explorer, entitled “Three New Plant Introductions from Japan”. There are 4 pages and some photos concerning udo (Aralia cordata) in the article “Udo : A new winter salad” (see pages 17-20 and the plates in the pdf below). This gives detailed growing instructions for “Kan udo” and “Moyashi udo” for harvesting during winter (October to May); these are cultivation techniques rather than udo varieties. Winter cultivation is more relevant to areas with relatively warm winters.
The other two plant introductions are Edgeworthia chrysantha as a fibre plant (for producing paper) and wasabi (Wasabia japonica).
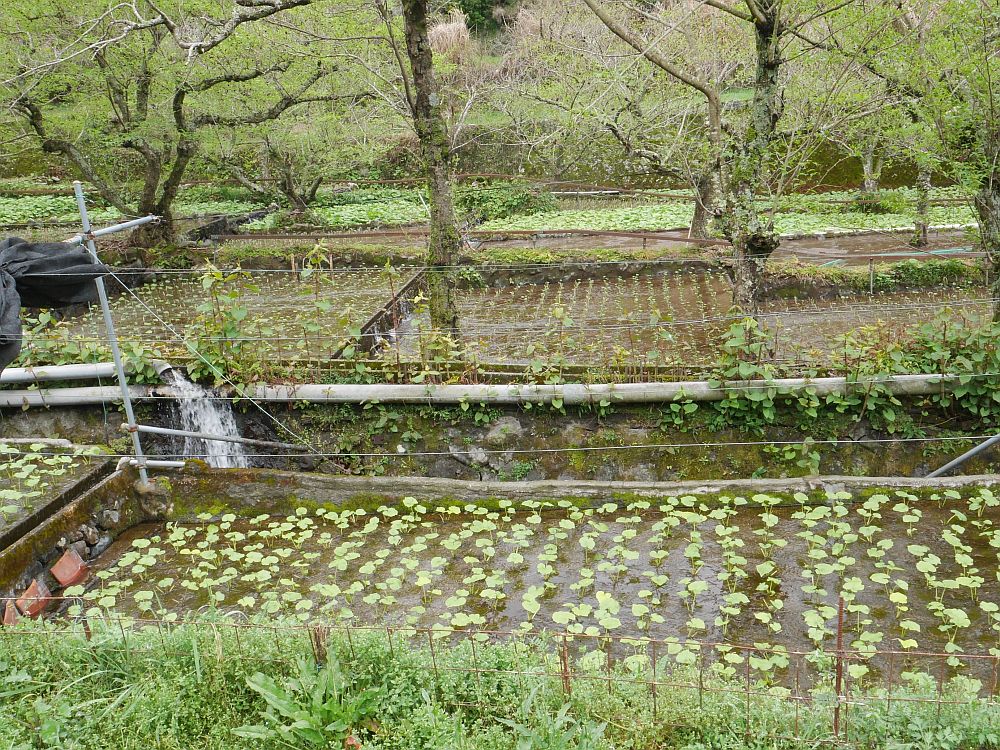
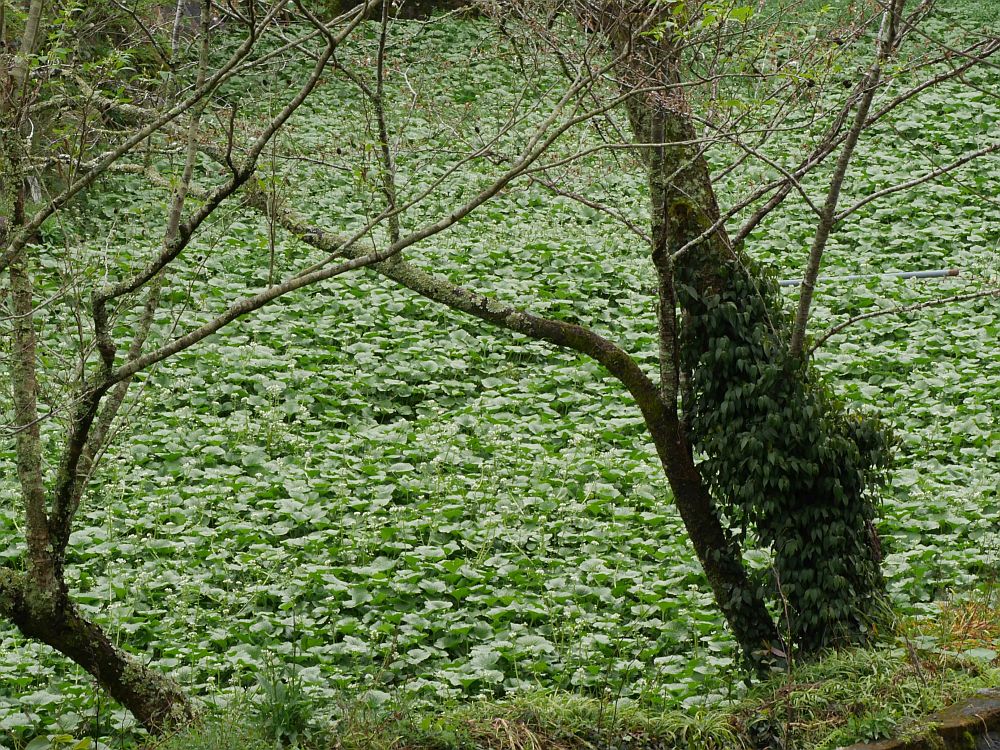
Kyle Dougherty posted on my Edimentals Facebook group in 2021 about the same program with a great picture of udo cultivation and wrote “Here’s an interesting story for the udo (Aralia cordata) fans out there. In 1902 the USDA imported some 25,000 improved udo plants into the United States from Japan for trialing as a new vegetable crop. Plants were grown at the experiment station in Rockville, MD until at least 1917, and were also distributed to private gardens around the country and the Chico field station in CA. The Rockville experiment station is long gone, and is now the site of Montgomery College, but I can’t help but wonder if any of these plants are still out there somewhere. It’s also kind of a bummer that it never really caught on despite the effort the USDA put into it.”
Here’s the document I discovered (pages and plates are repeated below)